16 - ذوبان الأنهار الجليدية
1Cause
2Consequences
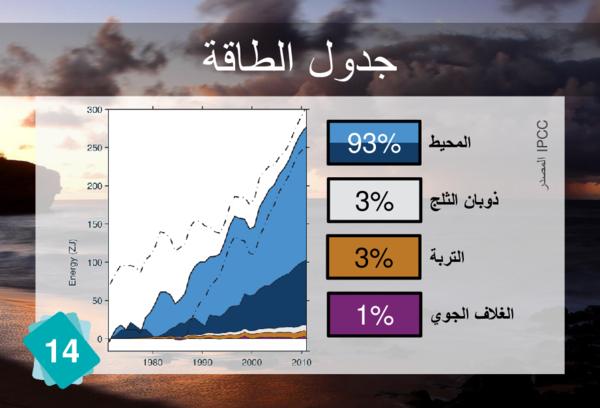
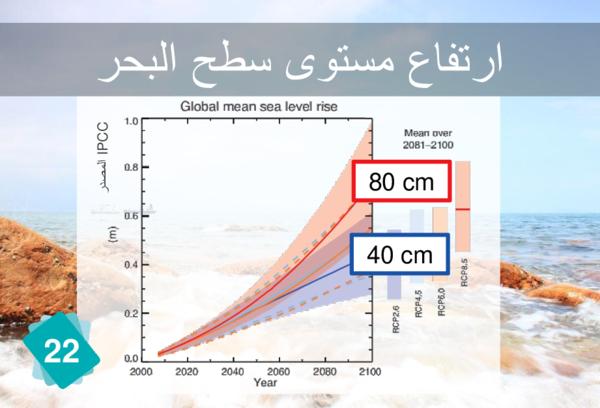
A melting of 100 gigatons of ice per year is equivalent to about 0.28 mm per year of mean sea level rise. Thus, 15 to 35% of sea level rise is linked to the melting of glaciers, according the IPCC scenarios. 30% to 35% is linked to the expansion of water. The remainder is linked to the melting of the ice caps.
Melting glaciers threaten water supplies. Indeed, the relative importance of glacier melt water in summer can be considerable, contributing for example to 25% of August flows in the basins draining the European Alps, with an area of about 105 km2 and only 1% glacial cover. Their disappearance could be catastrophic for cities located in valleys watered by rivers flowing down from the surrounding mountains and for freshwater fauna. Glacier meltwater also increases in importance during droughts and heat waves.
1Other possible consequence
It is possible, in certain circumstances of high heat, that very fast rapid melting of glaciers may cause flooding. But the real concern about these glaciers is that they are gradually disappearing, depriving downstream irrigation of a top-up in summer.