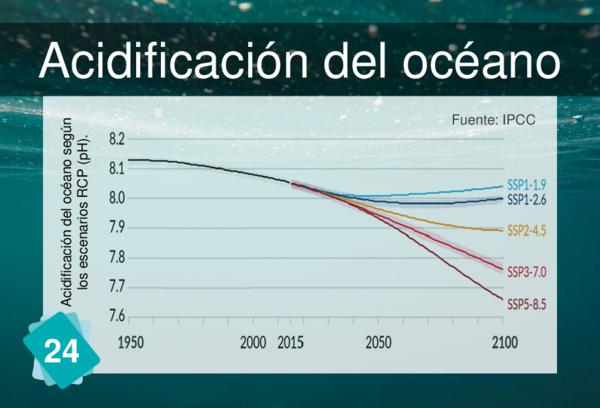
24 - Ocean Acidification
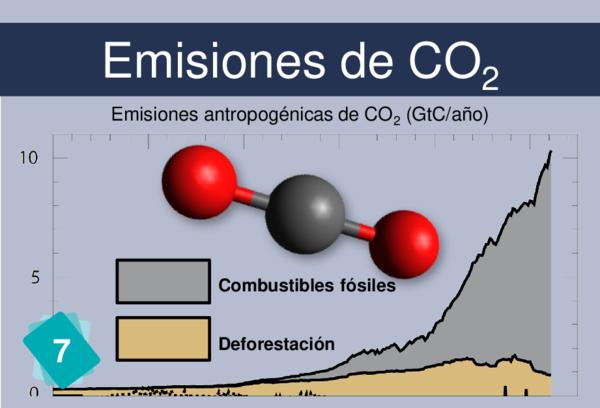
1Cause
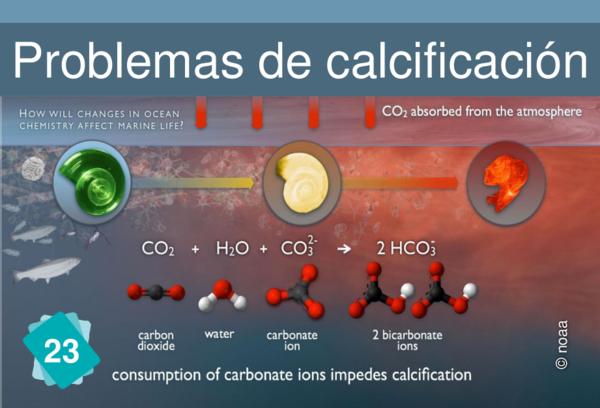
1Consequence
3Wrong causes
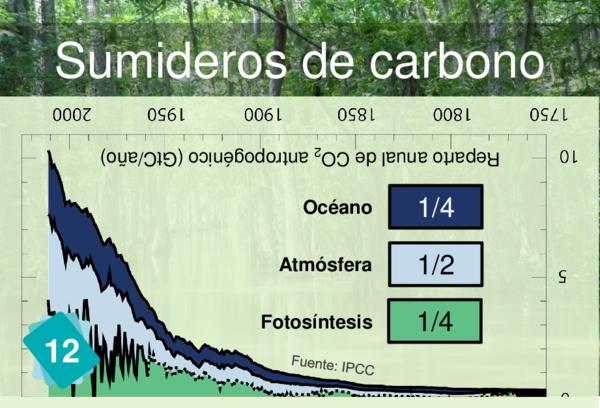
Why not but rather link Card 12 (Carbon sinks) to card 24. It is meant for it.
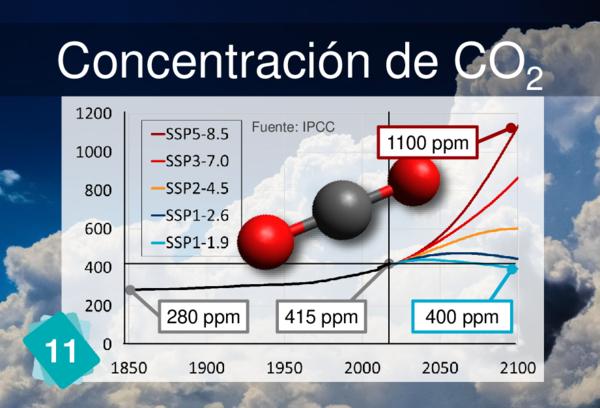
Players often identify CO2 concentration as a cause for ocean acidification. But it is more logical to link back to carbon sinks.
The increase of water temperature is not linked to ocean acidification, at least for the time being. In the long term (over several centuries), as it heats up, the water will lose its capacity to dissolve atmospheric CO2 and will become less efficient as a carbon sink. So the increase in water temperature will inhibit, to some extent, ocean acidification.