12 - Kohlenstoffsenken
2Causes
These two cards can be put border-to-border in order to reconstitute the original graph.
Ask the participants: "Have a look at card 12. What do you notice ? - It's written upside down - Exact. This is an enigma. The answer to it is on the table."
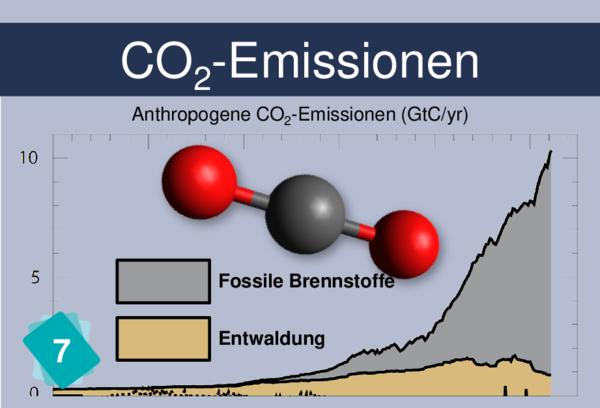
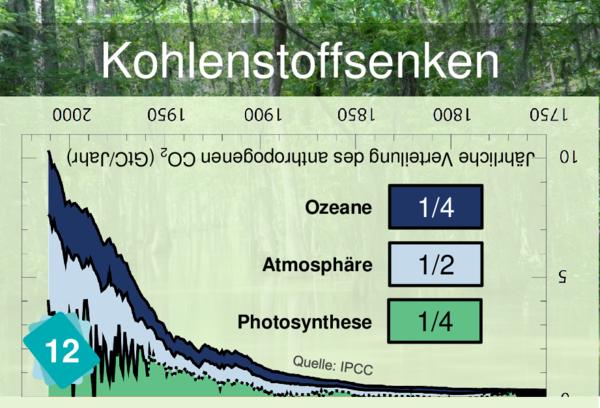
When they have found that 12 and 7 go together, then explain the resulting graph: it shows where the CO2 comes from and where it goes to. This is why the outer curves are symetricals. Each year, the CO2 emitted by Human beings has to go somewhere. If it's not in the carbon sinks, then it's in the atmosphere.
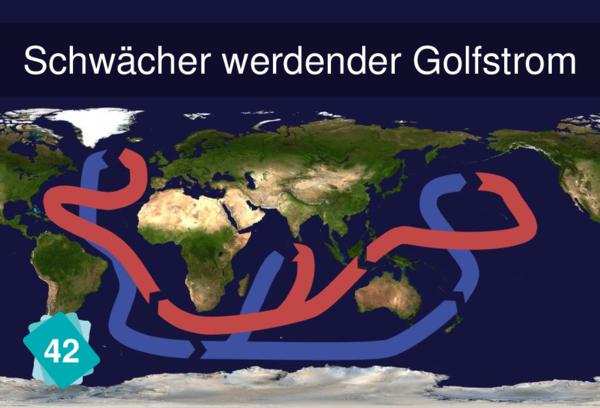
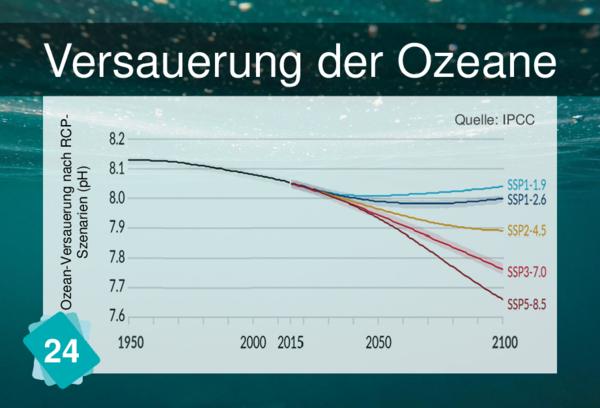
CO2 is absorbed at the surface of the ocean. Thermohaline circulation helps mix watersurface and deep ocean which is essential to the absoption of CO2 by the ocean.
2Consequences
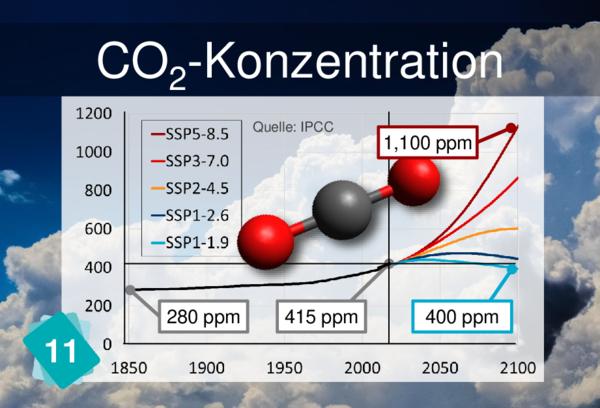
the card n11 represents the concentration in CO2, understood in the atmosphere (it's written behind the card).
The word "Ocean" is written on both sides.
3Other possible causes
Participants often think that deforestation reduces carbon sinks. In reality, the impact is minimal because deforested areas represent a very small part of the total forest area. Moreover, a mature forest has reached its equilibrium and no longer absorbs carbon. Therefore, as mainly mature forests are deforested, this does not impact carbon sinks. On the other hand, the amount CO2 released is very high.
It doesn't matter if this link is not made, but it is true that agriculture can improve storage capacity through photosynthesis. This is the 0.4% principle (if we increased the soil's capacity to sequester carbon by even 0,4%, we would have a significant impact on CO2).
If a lack of rain occurs while plants are growing, there is less photosynthesis and therefore a reduction in capacity of the carbon sink. In Europe, in 2018, carbon sinks declined by 18%.
1Other possible consequence
Studies have shown that yields increase with increased CO2, but that the nutrient content of vegetables is reduced as a result, because trace elements are not more abundant when yields increase.
1Wrong cause
It can be argued that CO2 emissions take place before reaching carbon sinks. But the opposite link has our preference.
1Wrong consequence
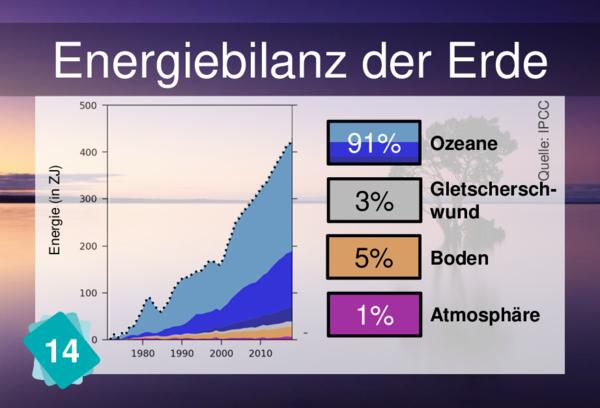
The idea here is not to say there is no link between these two cards, but to make sure they are not mixed up. The carbon sinks card tells us where the carbon goes. The energy budget card tells us where the excess energy goes. Both distribute something, but not the same thing. To make it even more confusing, the atmosphere and the ocean are present in both.