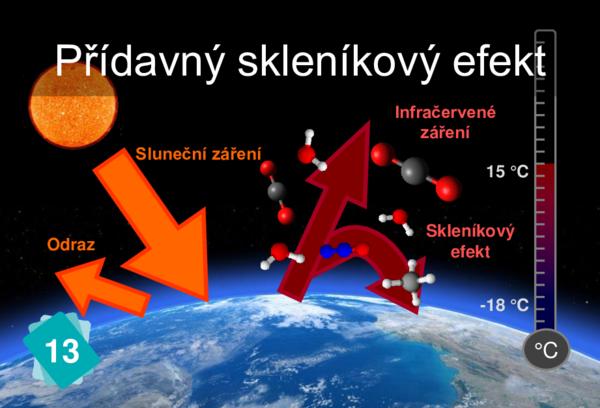
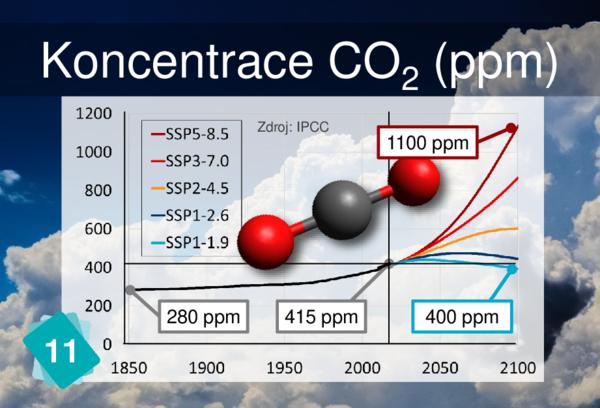
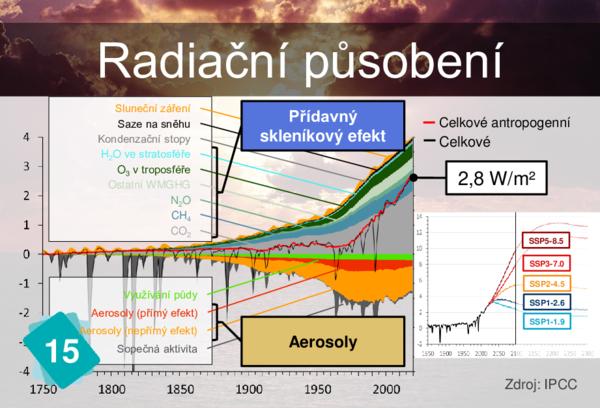
13 - Zesílený skleníkový efekt
2Causes
the "G" and the "H" on card 9 relate to "GreenHouse" on card 13.
You can recognize the molecules of the different GHGs on the card 13 : H2O (red and white), CO2 (grey and red), CH4 (grey and white), nitrious (blue and red).
1Consequence
1Other possible cause
The permafrost card can be linked either to Other GHGs or to Additional Greenhouse Effect. The Other GHGs card is about GHGs emitted by human activities, while the methane in permafrost is not of human origin.
1Wrong cause
This link would mark confusion with the amplifying effect due to albedo. The white sea ice melts to reveal a darker surface underneath and the extra energy absorbed warms the Earth. This mechanism is called albedo and has nothing to do with the greenhouse effect. It belongs to the orange arrows on card 13, not to the red arrows.