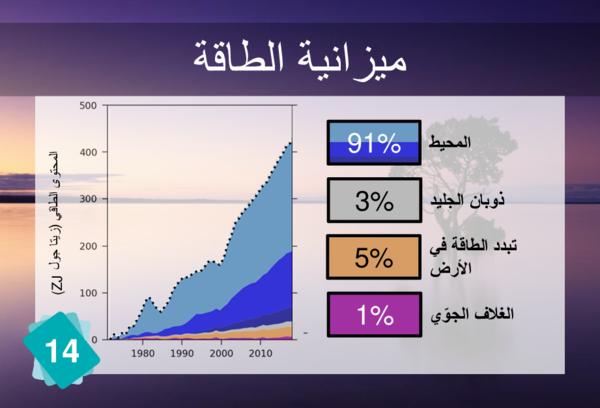
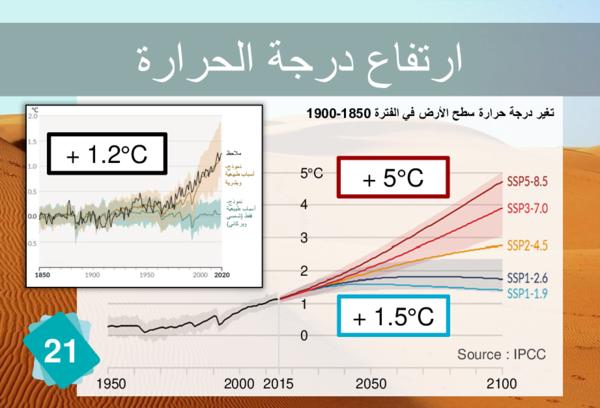
21 - Rising Temperatures
1Cause
As mentionned on card 21, this is the temperature of the air, above ground, in average on the Earth.
5Consequences
In northern countries, a little increase in temperature can lead to better yields, but in southern countries, it's the contrary: Any degree warmer is a decrease in yields.
2Other possible consequences
The vectors of disease card is generally linked to the Terrestrial Biodiversity card because disease vectors are a sub-part of biodiversity, but it can also be linked to the same causes as the biodiversity card, i.e. Disruption of the Water Cycle and Rising Air Temperatures.